Introduction
In today's modern world, electrical power systems play a crucial role in providing energy to meet the growing demands of society. One key aspect of power systems is maintaining the stability and reliability of the electrical grid, which includes ensuring that the frequency of the system remains within acceptable limits. Frequency regulation is essential to maintain the balance between power generation and consumption, and diesel generators are often used as a reliable and effective solution for this purpose. This article will delve into the details of diesel generators for frequency regulation, discussing their role, operation, advantages, and challenges.
Role of Diesel Generators in Frequency Regulation
Frequency regulation is the process of maintaining the frequency of an electrical grid at a stable level. In an interconnected power system, the balance between power generation and consumption must be maintained to ensure that the frequency remains within the acceptable range, typically around 50 or 60 Hertz, depending on the region. When there is an imbalance between generation and consumption, the frequency of the system can deviate from the nominal value, leading to potential disruptions in power supply and damage to electrical equipment.
Diesel generators play a crucial role in frequency regulation by providing fast and reliable response to changes in power demand or generation. These generators can be quickly started and ramped up to supply additional power to the grid when needed, helping to stabilize the frequency and maintain system reliability. Diesel generators are particularly well-suited for frequency regulation due to their flexibility, efficiency, and ability to operate independently of other power sources.
Operation of Diesel Generators for Frequency Regulation
Diesel generators operate on the principle of converting the chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into electrical energy through an internal combustion engine. The basic components of a diesel generator system include the diesel engine, alternator, fuel system, cooling system, and control system. When a diesel generator is called upon to provide frequency regulation, the control system monitors the frequency of the grid and adjusts the output of the generator accordingly.
During normal operation, a diesel generator runs at a constant speed to generate electricity at a fixed frequency. However, when the frequency of the grid deviates from the nominal value, the control system of the generator senses this change and adjusts the engine speed to match the grid frequency. By increasing or decreasing 500KW Diesel Generator For Sale of the generator, the diesel engine helps to stabilize the frequency of the electrical grid and restore the balance between generation and consumption.
Advantages of Diesel Generators for Frequency Regulation
Diesel generators offer several advantages when used for frequency regulation in electrical power systems. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Fast Response Time: Diesel generators can be started and ramped up to full capacity within seconds, providing a rapid response to changes in power demand or generation. This fast response time is crucial for maintaining the stability of the grid and preventing frequency deviations.
2. High Efficiency: Diesel generators are known for their high efficiency in converting fuel into electrical energy. This efficiency ensures that diesel generators can provide reliable and cost-effective frequency regulation services while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
3. Independent Operation: Diesel generators can operate independently of other power sources, making them suitable for providing backup power and frequency regulation services in isolated or remote areas. This independence allows diesel generators to respond quickly to changes in system conditions without relying on external support.
4. Scalability: Diesel generators are available in a wide range of sizes and capacities, making them highly scalable for different applications and power requirements. Whether used for standby power or continuous operation, diesel generators can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the electrical grid.
5. Reliability: Diesel generators are known for their robust construction and durability, making them a reliable source of power for frequency regulation. With proper maintenance and servicing, diesel generators can provide years of dependable service to ensure the stability of the electrical grid.
Challenges of Diesel Generators for Frequency Regulation
While diesel generators offer several advantages for frequency regulation, they also pose certain challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance. Some of the challenges associated with diesel generators for frequency regulation include:
1. Environmental Impact: Diesel generators emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO) during operation, contributing to air pollution and environmental degradation. To mitigate the environmental impact of diesel generators, emission control technologies such as exhaust gas treatment systems can be used.
2. Fuel Availability and Cost: Diesel fuel is a fossil fuel that is subject to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. The availability and cost of diesel fuel can impact the operation and economics of diesel generators for frequency regulation, especially in remote or off-grid locations where fuel delivery may be challenging.
3. Noise and Vibration: Diesel generators can generate high levels of noise and vibration during operation, which can be disruptive to nearby residents or sensitive equipment. Proper acoustic insulation and vibration damping measures are necessary to reduce the noise and vibration produced by diesel generators.
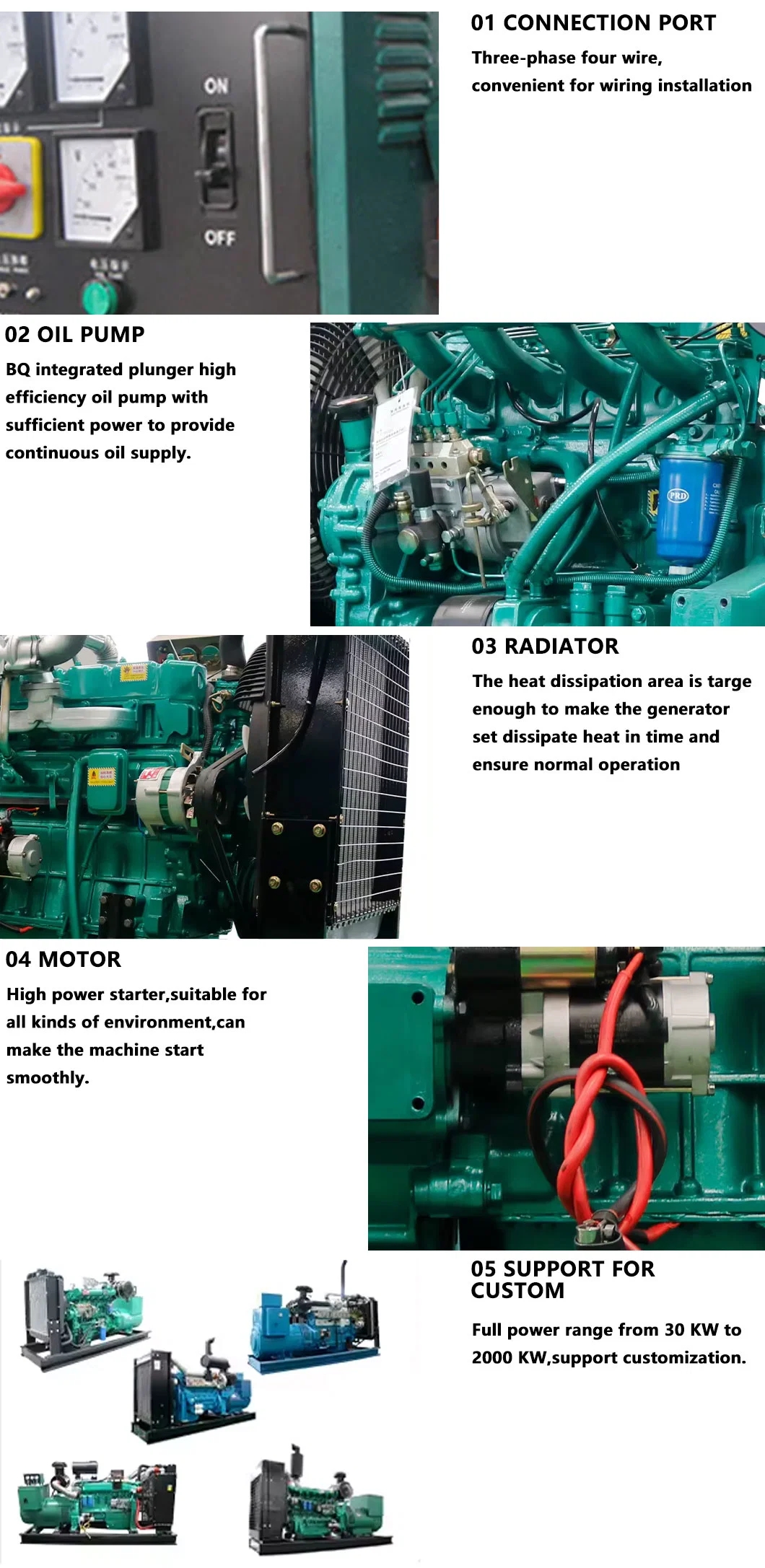
4. Maintenance Requirements: Diesel generators require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Scheduled maintenance tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, and engine inspections are essential to prevent breakdowns and prolong the lifespan of diesel generators.
5. Limited Fuel Efficiency at Low Loads: Diesel generators are most efficient when operated at high loads close to their rated capacity. Running diesel generators at low loads for extended periods can reduce fuel efficiency and increase emissions, leading to higher operational costs and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Diesel generators play a crucial role in frequency regulation in electrical power systems, providing fast and reliable response to changes in power demand or generation. With their high efficiency, scalability, and independence of operation, diesel generators offer several advantages for maintaining the stability of the grid. However, challenges such as environmental impact, fuel availability, noise, and maintenance requirements need to be addressed to ensure the optimal performance of diesel generators for frequency regulation. By understanding the role, operation, advantages, and challenges of diesel generators, power system operators can make informed decisions on incorporating these generators into their frequency regulation strategies.
